| Department of Physics | University of Durham | Level One |
Recently the results of the Hipparcos space astrometry mission have become available. Access the Hipparcos database via the Web and find a very accurate value for the proper motion of Barnard's star.
How does the Hipparcos value and the quoted uncertainty compare to your value and uncertainty?
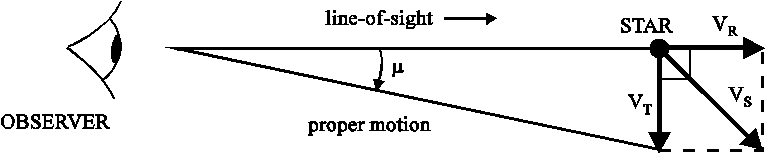
Tangential velocity, (VT), of a star is the across the line-of-sight velocity expressed in units of kms-1. VT can be derived from the proper motion (mu) and the distance (d) in parsecs of the star via
VT [kms-1] = 4.74 mu [arcsec yr-1] d [pc] You should confirm the unit conversion factor of 4.74.( 1 radian = 206265 arcsecond, 1 parsec = 206265 AU, 1 AU = 149,600,000 km )
The current distance to Barnard's star is 1.821 pc.
What is the tangential velocity of Barnard's star in units of kms-1 ?
The 3D Space Motion, (VS), is derived from VR and VT, via, VS2 = VR2 + VT2. The angle to the line-of-sight, theta is given by tan(theta) = VT/VR.
Barnard's star has a radial velocity of -111 kms-1. The negative sign indicates that the motion is towards the observer.
What is the 3D space velocity of Barnard's star?
What is the angle that the space velocity makes with the line-of-sight?
What is the closest approach of Barnard's star to the Sun and when will this take place?
You will find Robert Matthew's article on the Close Approach of Stars in the Solar Neighbourhood helpful for this analysis.
![]()
This page is maintained by jrl. Last updated: 1998-Jun-06